
Menu
Featured Patients Having Scoliosis with Before & After Photos (Scroll down on the page to see pictures)
How I Healed My Kid’s Scoliosis- NATURALLY – (no braces, no surgery!)
Scoliosis and Dental Occlusion: A Review of the Literature (When the tongue is tied, it does not sit at the palate, and cannot do its job which is to widen and shape the palate so all teeth fit; even the wisdom teeth. Teeth crowding and malocclusions occur since the palate is narrow. It also mentions the correlation between plagiocephaly and scoliosis. Plagiocephaly is a common sign of ties in babies.)
According to the article, Dr. Jones said research is now showing SIDS is a form of obstructed sleep apnea, which leaves infants vulnerable. “Research is showing that tongue restriction may be linked with sleep apnea in older children and adults, so it’s possible there is a link in infants presenting with Annabelle’s symptoms. It’s an emerging theme we need to learn more about. Stanford University is showing that ties have an effect on airways and growth of the jaws and face. It is trailblazing research,” she said
Our saliva contains digestive enzymes and it is the first process of breaking down our food. Without adequate breakdown in the mouth, we produce extra acid to break down the proteins in the stomach. This acid often leads to GERD. Many infants are often placed on special formulas due to food sensitivities/acid reflux and unaware that the underlying root cause may be tongue, lip, or buccal ties. See the articles below:
The job of the vagus nerve is to help with rest and digestion.
A part of the vagus nerve is found at the roof of the mouth behind your front teeth. When we put our tongue there, usually by instinct, it stimulates our vagus nerve and calms tension. That is the correct position our tongue should be in. But, if there is a tongue tie or someone is a mouth breather their tongue cannot reach this spot. This can cause tension, anxiety, and chronic stress.
Chronic bedwetting is often related to sleep apnea because there is not enough oxygen for all systems so the body diverts oxygen from non-essential functions to the brain. Therefore, urine control becomes a low priority.
Mouth breathing, which often accompanies tongue ties, causes inflammation in the adenoids and tonsils due to unfiltered, dry, cold air that enters the mouth.
If your baby has their rear in the air while sleeping on their belly this may indicate they are trying to create space to breathe better.
Tongue ties typically are accompanied by a lip tie, high palate, and recessed chin. While tongue tie, lip tie, high palate, and recessed chin are exclusive of one another, their combination of all of these can contribute to significant issues with breastfeeding.
High palates make it difficult for the tongue to properly elevate to the roof of the mouth to compress the nipple for breastfeeding (or bottle feeding) and thus can hinder the tongue’s ability in contributing to proper jaw development. A recessed chin makes it difficult to maintain and hold a latch, due to potential misalignment of the jaw. A lip tie (which is further discussed below) contributes to the increased air intake, resulting in reflux and colic.
When an infant tries to lift its tongue and the center stays tethered down, it creates the heart shape This shape may or may not go away once the tie is released. Cutting that band somewhere in the middle doesn’t remove the portion of the band inside the tongue. That can still change the shape of the tongue but typically doesn’t affect function.
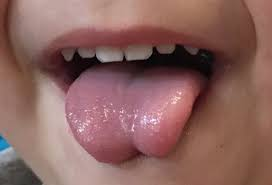
Very often individuals are compensating with their lips (using more gross motor movements) while chewing since their tongue’s fine motor movements are limited in their mobility due to being tethered from a tie.
Due to the tongue and/or lip impairment caused by ankyloglossia, the oral structures and airway tend to be smaller than normal. If the oral tissue begins to sag, Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may result.
This condition occurs when oral tissue blocks the airway entirely multiple times during the night, often for 10 seconds or more. OSA interferes with restful sleep, and can even contribute to the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
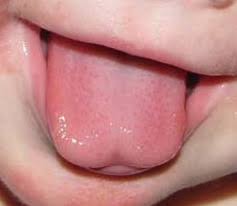
Professionals assessing babies for tongue-ties should assess elevation, lateralization, and extension. Elevation can most easily be assessed when a baby cries. With the mouth wide open, the tongue tip should lift up to at least the mid-mouth. In tongue-tied babies, the tongue often stays quite flat on the floor of the mouth or the edges curl up to form a bowl shape or “V” shape. Babies should be able to poke their tongue tip out well over the bottom lip when the bottom lip is stimulated. When the assessor runs their finger along the top ridge of the bottom gum the tip of the baby’s tongue should follow the finger so the tongue sweeps side to side (lateralization).
Some assessors perform a suck assessment by placing their finger in the baby’s mouth (pad side up, nail side down) and feeling how the baby is cupping and using their tongue. Assessors sweep their fingers under the baby’s tongue so they can feel the extent of the tongue tie and the tongue will also be lifted to visualize the frenulum. The appearance of the frenulum is also documented including the shape of the tongue tip, where it attaches to the floor of the mouth and the underside of the tongue, and how long and stretchy it is.
Fascia is the connective tissue that holds your insides in! It is incredibly strong and important. All of the frena in the mouth are made of fascia, including the frenum under the tongue. Since muscles are responsible for moving the bones in our body, so does the tongue. Being a muscle, it moves bone (your teeth).
Due to the low tongue position, often high palate, and the upper lip not flanging out completely over the nipple, bottle, or breast, your baby cannot make a good seal and loses suction, you can hear clicking sounds. Also, very loud drinking, gulping it down, and choking. Complaints of swallowing air. The swallowed air needs to go somewhere; it goes up or down. Burping, hiccough, spitting, windy, colic. GER or reflux with or without spitting (hidden reflux). In hidden reflux the baby tries to keep the milk down by swallowing again, sometimes forgetting to breathe momentarily. During feeding, it can be very uncomfortable for the baby and can become restless. It’s difficult to put the baby down to sleep. Parents walk with their baby until symptoms subside. The baby can experience pain from the stomach acid in the esophagus. GERD. Sometimes medication is given which lowers stomach acid. Thrush is often confused with tongue-tie problems. Although you can see it both at the same time. The tongue may have debris in the papilla (from the day of birth) due to the fact that the tongue hardly touches the palate so it doesn’t “rub clean”. Pinching and stabbing pain can be from thrush or compensating behavior from tongue and lip tie. With a tongue tie, you can see white debris on the posterior part of the tongue behind the tongue tie, the front of the tongue rubs clean against the inside of the upper maxilla. Thrush is a “pearl white” shine or white plaques on the inside of the lips and on the mucous membranes of the inside of the mouth.
*Note that not all symptoms have to be present at the same time.
Sometimes restless drinking, when the baby lets go often and makes clicking sounds are attributed to having thrush (candida infection), and when feeding is painful for the mother. However, both tongue tie and thrush can be present. When there is thrush, there is sometimes little to see on the nipples and areola of the mother. On the baby, you see white plaques on the mucous membranes on the inside of the lips and cheeks in the mouth. Often a “two-tone” tongue is seen. Due to the tongue tie, the front part of the tongue wipes clean (against the inside of the upper jaw) and the back part of the tongue does not, because the tongue is “tied” low in the mouth. You see a white deposit in the taste buds which can be confused with thrush.
It takes less than 5 grams of pressure to influence the cranial bones’ shape and motion. So placing a tight headband that constricts the cranium will not only change the shape of the head but will decrease the movement of the cranial bones and negatively impact the primary respiratory mechanism. Many parents who have little girls who are bald for a long time will want to always have a headband on their baby since they can not clip on bows to her hair. This will always constrict the movement of the cranial bones and work towards altering the shape of the cranium. Typically a headband will wrap around the occiput, temporal, sphenoid, and frontal bones. Even slight alterations in the shape or motion of the occiput can cause misalignments in any other cranial bone. This again will cause adhesions in the dura and affect the nutrient saturation of the nervous system. Keep the headband or bow in your bag and only slip it on for pictures and then take it right back off. Look for red marks and signs of the bow on the head after you take it off. The more marks and redness you see left behind after the bow is off, tells you there is more pressure being applied by the headband. Bows and headbands look cute but have a huge impact on the shape and motion of the cranium.
It takes less than 5 grams of pressure to influence the cranial bones’ shape and motion. So placing a tight headband that constricts the cranium will not only change the shape of the head but will decrease the movement of the cranial bones and negatively impact the primary respiratory mechanism. Many parents who have little girls who are bald for a long time will want to always have a headband on their baby since they can not clip on bows to her hair. This will always constrict the movement of the cranial bones and work towards altering the shape of the cranium. Typically a headband will wrap around the occiput, temporal, sphenoid, and frontal bones. Even slight alterations in the shape or motion of the occiput can cause misalignments in any other cranial bone. This again will cause adhesions in the dura and affect the nutrient saturation of the nervous system. Keep the headband or bow in your bag and only slip it on for pictures and then take it right back off. Look for red marks and signs of the bow on the head after you take it off. The more marks and redness you see left behind after the bow is off, tells you there is more pressure being applied by the headband. Bows and headbands look cute but have a huge impact on the shape and motion of the cranium.
When your baby is sleeping, slowly pull down on their chin as the mouth starts to open. The tongue should be lightly suctioned to the roof of the mouth and make a clicking noise when you open it all the way as the tongue should release from the roof of the mouth.
A tongue tie can cause bruxism your jaw muscles tightens to compensate for the loss of the normal healthy support your tongue should provide. Grinding is usually sleep disorder related too. The brain signals grinding in order to stimulate breathing.

